Publications

Patch-Free 3D Medical Image Segmentation Driven by Super-Resolution Technique and Self-Supervised Guidance (MICCAI 2021)
Hongyi Wang, Lanfen Lin, Hongjie Hu, Qingqing Chen, Yinhao Li, Yutaro Iwamoto, Xian-Hua Han, Yen-Wei Chen, Ruofeng Tong
In this paper we propose a low-cost 3D segmentation framework which can realize HR segmentation with LR input. Thus, patch-sampling is no longer needed and the model can have the global context when training. Experiments show that our model outperforms patch-based methods with a 4x higher speed.
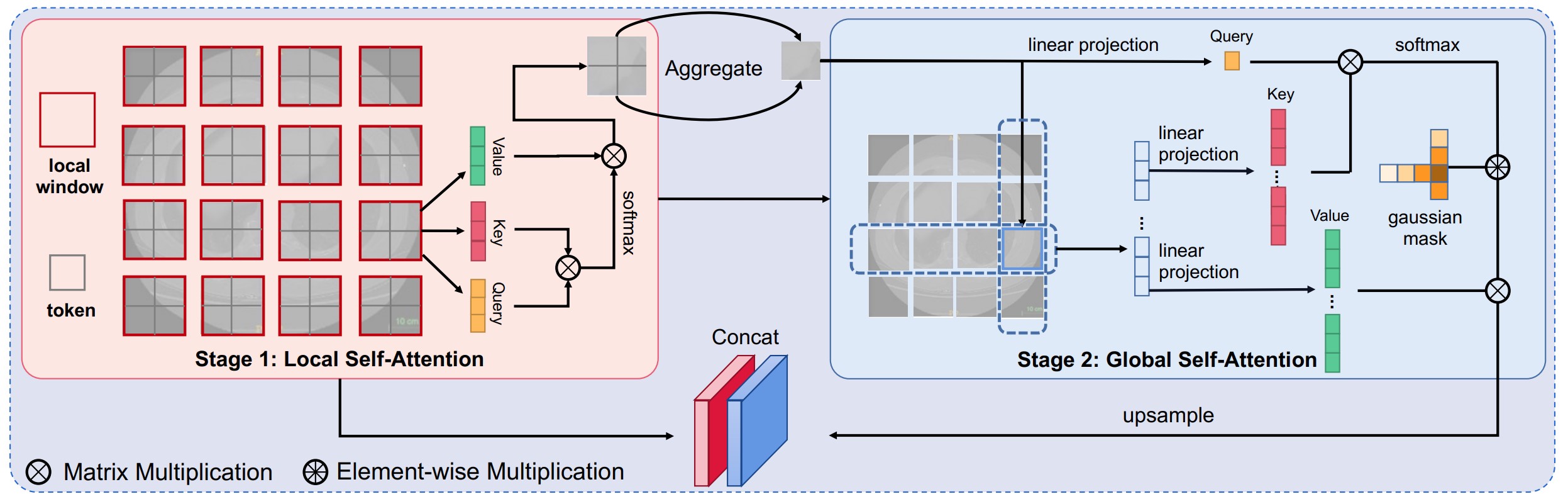
Mixed Transformer U-Net For Medical Image Segmentation (ICASSP 2022)
Hongyi Wang, Shiao Xie, Lanfen Lin, Yutaro Iwamoto, Xian-Hua Han, Yen-Wei Chen, Ruofeng Tong
In this paper we propose a new Vision Transformer module to simutaneously model local and global dependecies. The self-attention is split into fine-grained local SA and coarse-grained global SA with a gaussian mask further added on it. Experiments show that our model achieved sota performance on two datasets.

CubeMLP: An MLP-based Model for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis and Depression Estimation (ACM MM 2022)
Hao Sun, Hongyi Wang, Jiaqing LIU, Yen-wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this paper we propose a simple yet efficient pure-MLP multimodal fusion technique named CubeMLP. CubeMLP fuses the multimodal input in sequence, modality and channel dimensions repectively, achieving SOTA performance on CMU-MOSI, CMU-MOSEI and AVEC2019 with a much lower complexity.
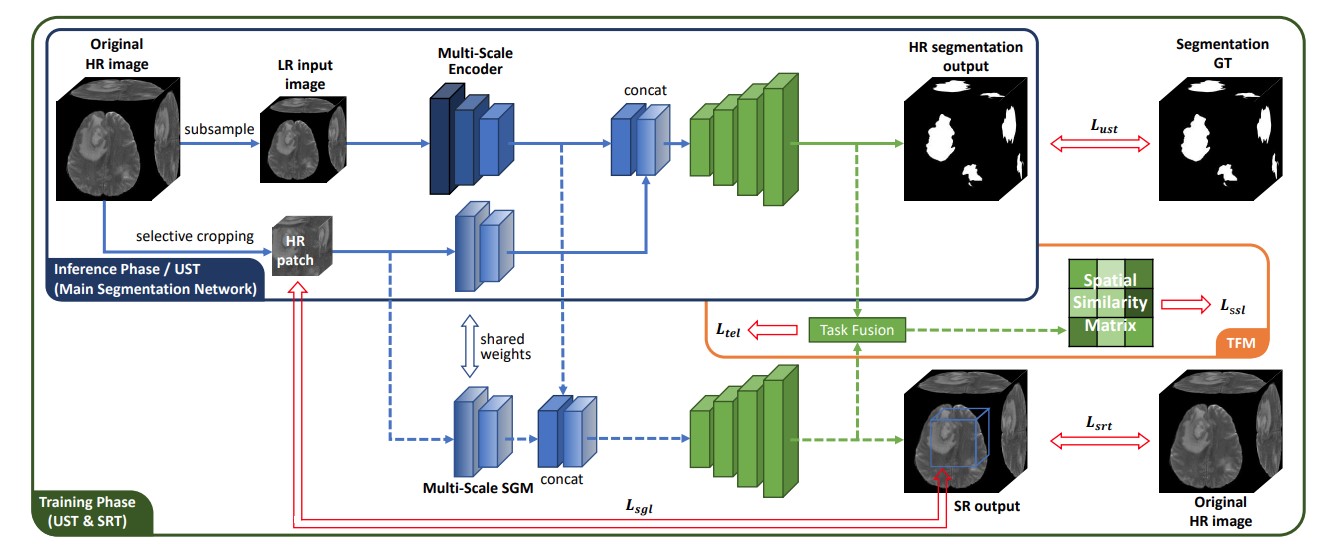
Super-Resolution Based Patch-Free 3D Medical Image Segmentation with High-Frequency Guidance
Hongyi Wang, Lanfen Lin, Hongjie Hu, Qingqing Chen, Yinhao Li, Yutaro Iwamoto, Xian-Hua Han, Yen-Wei Chen, Ruofeng Tong
This paper is the extended version of our MICCAI 2021 paper. The main improvements include a selective cropping algorithm for HR guidance patch, the use of multi-scale encoders, and test-time refinement based on the existing LR-HR image pair. This paper is finished in January 2022.
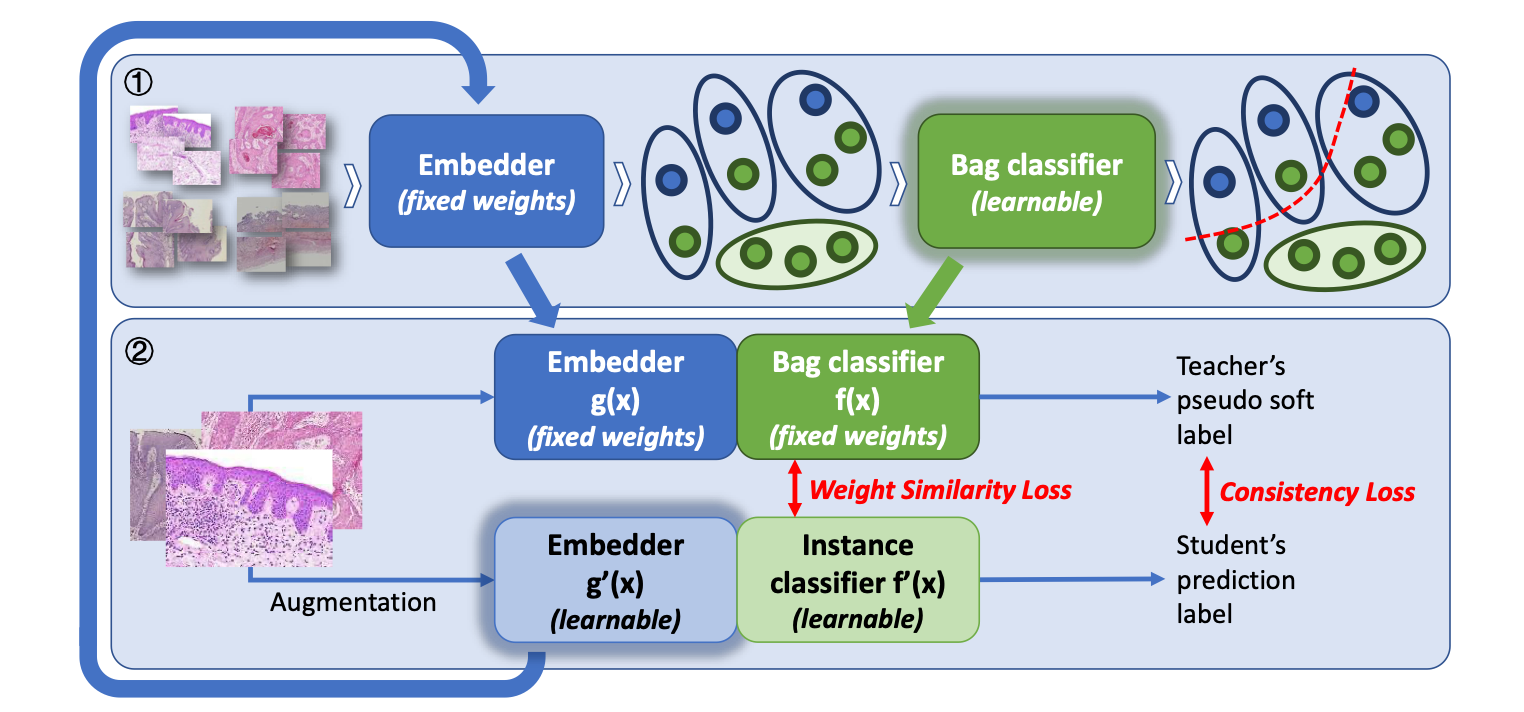
Iteratively Coupled Multiple Instance Learning from Instance to Bag Classifier for Whole Slide Image Classification (MICCAI 2023)
Hongyi Wang, Luyang Luo, Fang Wang, Ruofeng Tong, Yen-Wei Chen, Hongjie Hu, Lanfen Lin, Hao Chen
In this paper, we propose to solve the information propagation gap between the embedder and classifier in MIL with an iteratively coupled method. This elegant method view the entire MIL pipeline as an EM optimization problem, and is highly generalizable. We adopt ICMIL on different MIL backbones and achieved consistent improvements. The main branch of the repository holds the code for this method.

Rethinking Multiple Instance Learning for Whole Slide Image Classification: A Bag-Level Classifier is a Good Instance-Level Teacher (TMI, 2024)
Hongyi Wang, Luyang Luo, Fang Wang, Ruofeng Tong, Yen-Wei Chen, Hongjie Hu, Lanfen Lin, Hao Chen
In this extended journal version of ICMIL, we propose to use the instance aggregator in MIL backbones to generate confidence score for each instance's pseudo label, thereby improving the effectiveness of the embedder fine-tuning. A bag-level augmentation method is also added for the MIL training to realize a even higher performance. Check our code in the alternative branch of the repository.
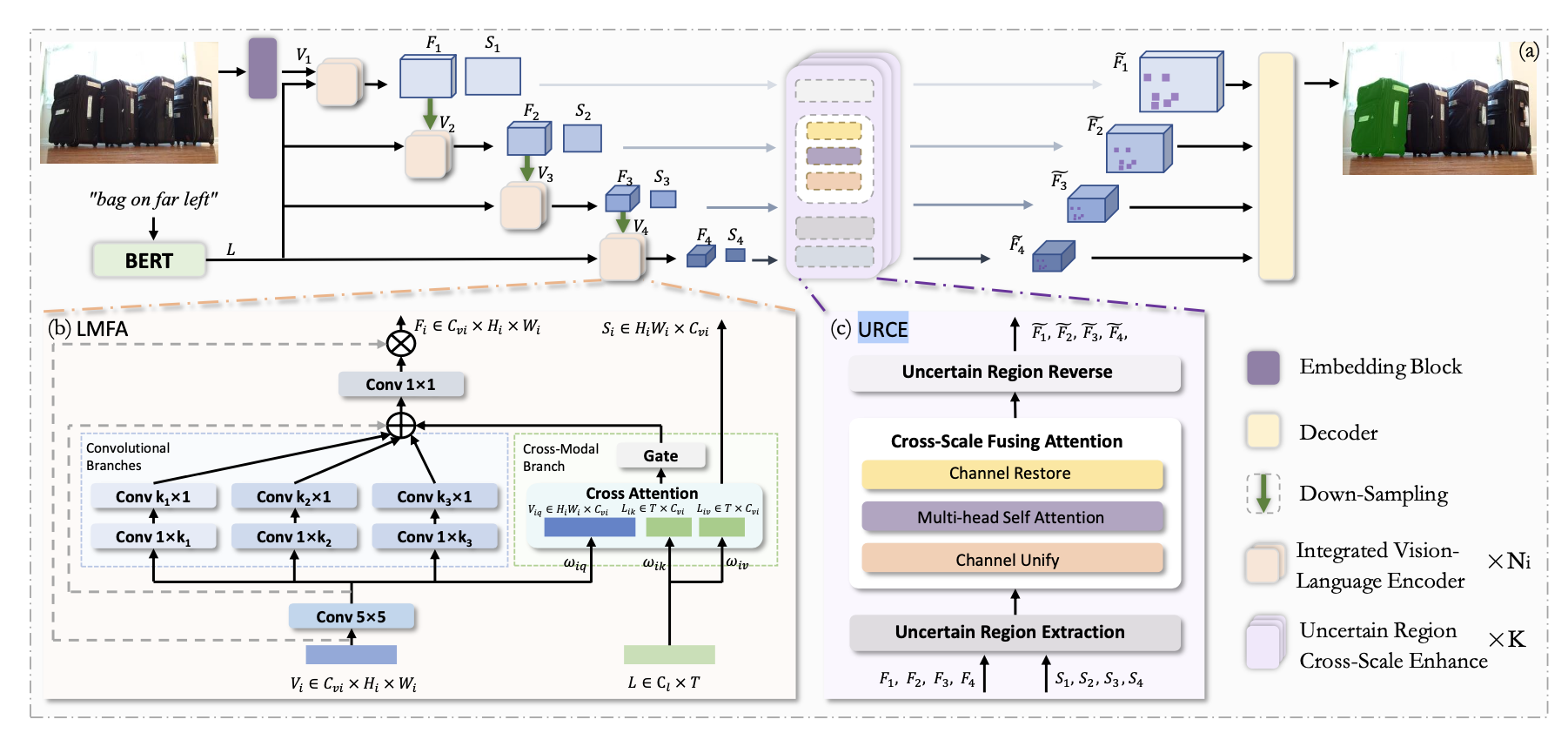
SLViT: Scale-Wise Language-Guided Vision Transformer for Referring Image Segmentation (IJCAI 2023)
Shuyi Ouyang, Hongyi Wang, Shiao Xie, Ziwei Niu, Ruofeng Tong, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this work, we propose a novel referring segmentation network named SLViT. SLViT introduces an effective encoder block for simutaneous feature extraction and cross-modal attention. Then, it proposes LMFA to exploit the multi-scale information to generate more comprehensive outputs. Furthermore, a novel URCE module is also proposed to find and refine the high uncertainty tokens based on the cross-scale information. SLViT achieves SOTA performance on three datasets.

MCKD: Mutually Collaborative Knowledge Distillation for Federated Domain Adaptation and Generalization (ICASSP 2023)
Ziwei Niu, Hongyi Wang, Hao Sun, Shuyi Ouyang, Yen-wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
MCKD combines UDA and DG with Federated Learning to achieve a higher performance while preserving the users' privacy. collaborative distillation strategy using multiple local models and a centralized model. Experimental results demonstrate its competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art methods on four datasets.
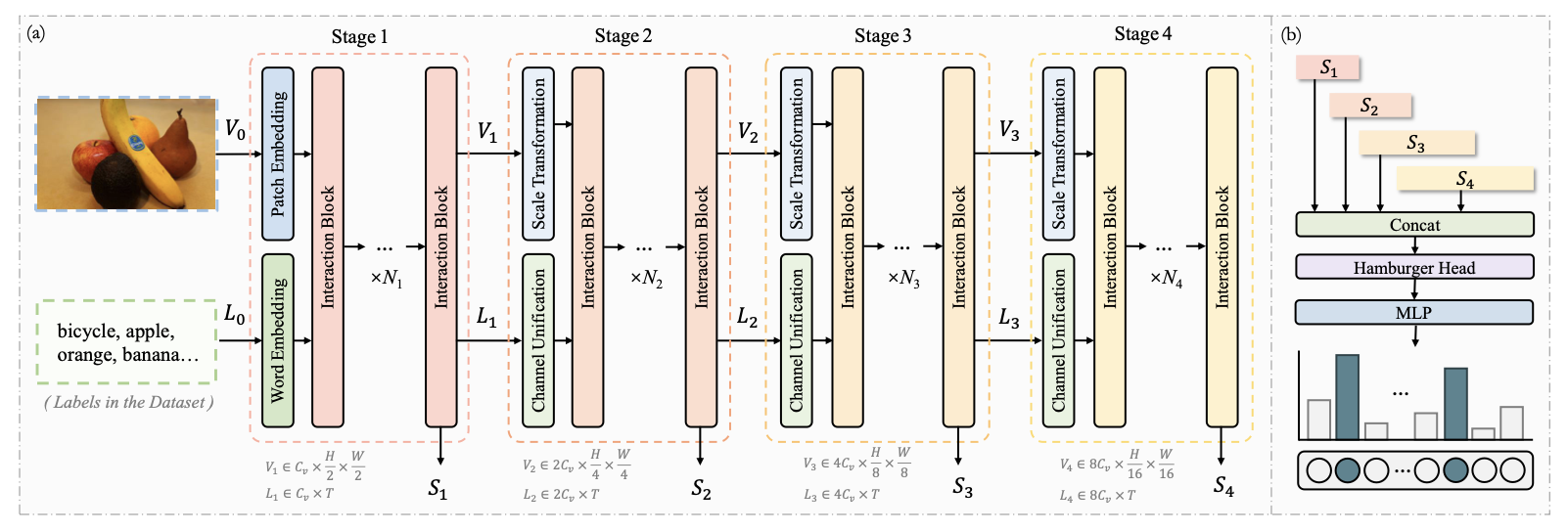
HSVLT: Hierarchical Scale-Aware Vision-Language Transformer for Multi-Label Image Classification (ACM MM 2023)
Shuyi Ouyang, Hongyi Wang, Shiao Xie, Ziwei Niu, Ruofeng Tong, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this work, we propose a multi-scale vision-language model named HSVLT for multi-label image classification. HSVLT features IVLA and CSA, of which the former is for joint updating of visual features, linguistic features, and multi-modal features considering interactive cross-modal cues, and the later is for leveraging complementary information from different scales for decision-making purposes. HSVLT achieves sota performance on three different datasets.
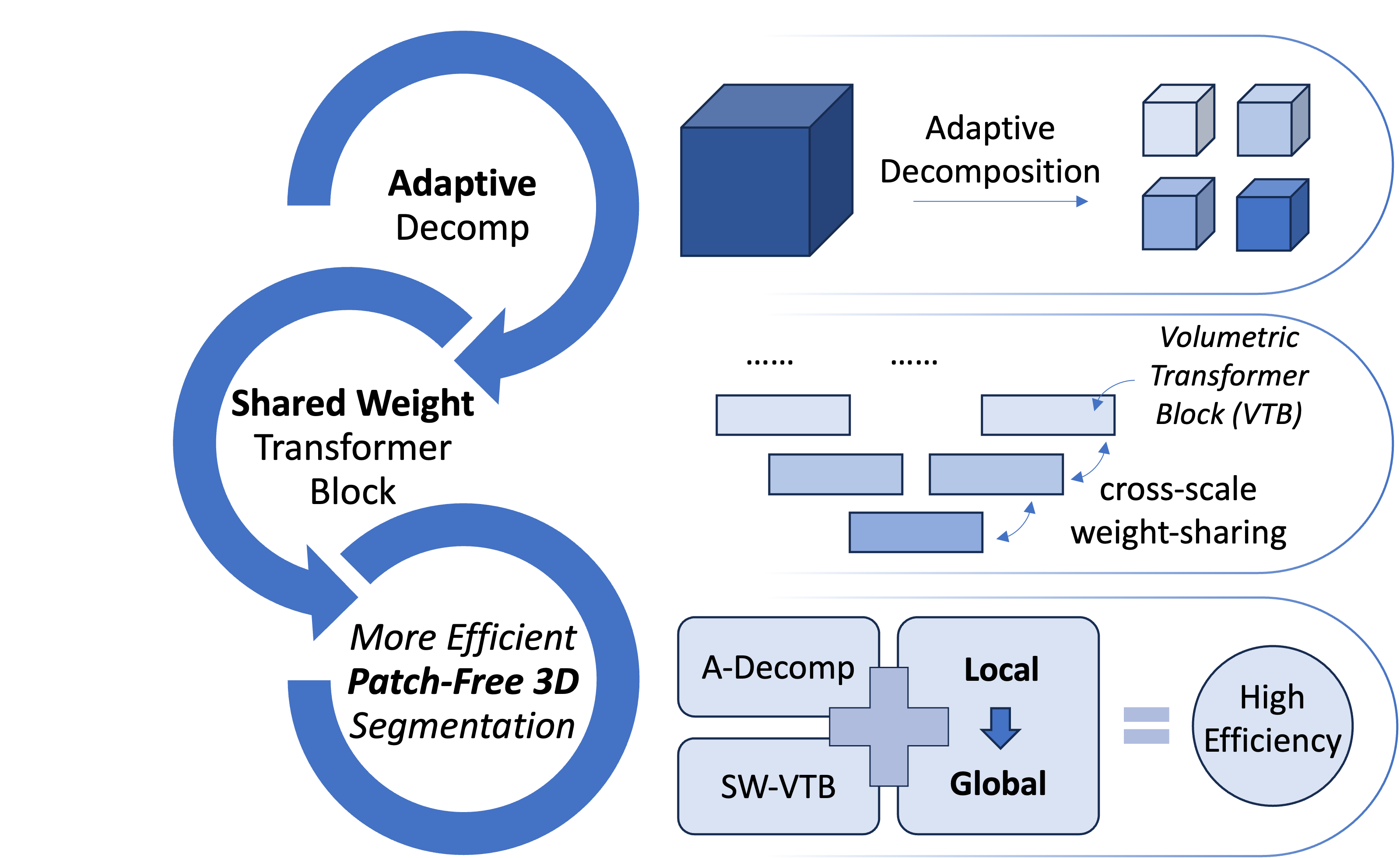
Adaptive Decomposition and Shared Weight Volumetric Transformer Blocks for efficient patch-free 3D medical image segmentation (J-BHI, 2023)
Hongyi Wang, Yingying Xu, Qingqing Chen, Ruofeng Tong, Yen-Wei Chen, Hongjie Hu, Lanfen Lin
In this paper, we propose a novel patch-free 3D medical image segmentation network named VolumeFormer. It features Adaptive Decomposition, which is the inproved learnable version of Holistic Decomposition, and Shared-Weight Volumetric Transformer Block, a lightweight 3D transformer block that can realize cross-scale weight-sharing. The experimental results demonstrate its efficiency and effectiveness.
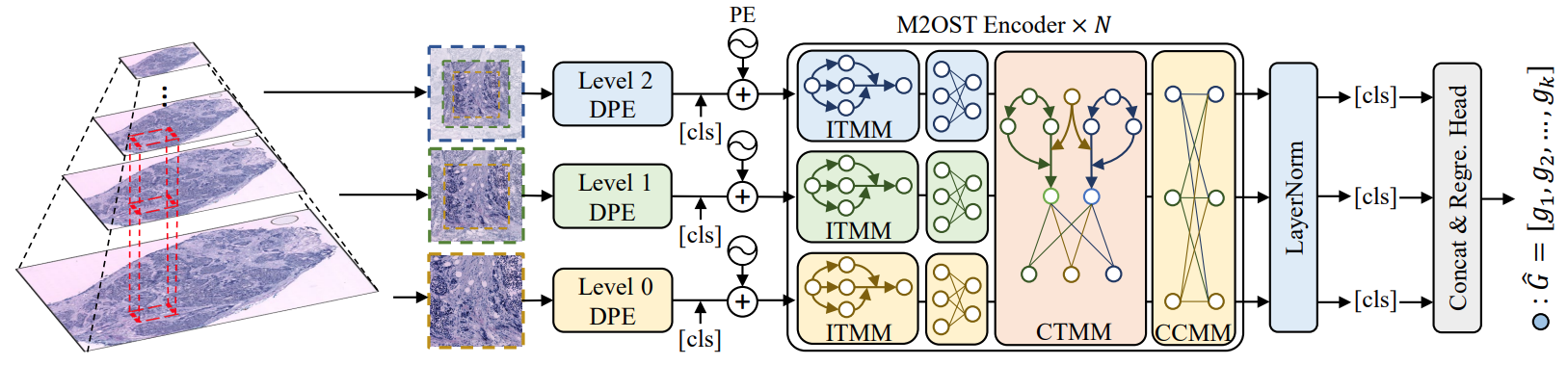
M2OST: Many-To-One Regression for Predicting Spatial Transcriptomics from Digital Pathology Images (AAAI 2025)
Hongyi Wang, Xiuju Du, Jing Liu, Shuyi Ouyang, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this paper, we propose a many-to-one regression transformer, M2OST, for Spatial Transcriptomics prediction. We also propose ITMM, CTMM, and CCMM to decouple the multi-scale modeling process in M2ORT, leading to notable savings in computational cost without compromising performance.
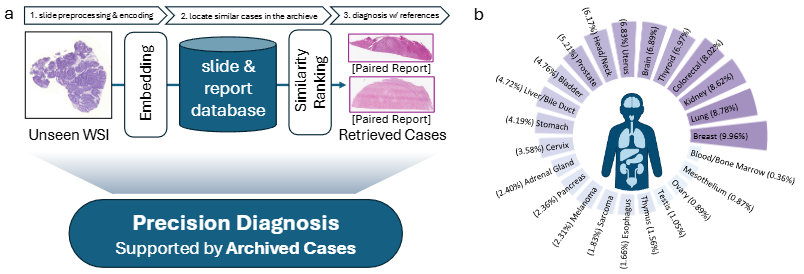
Accurate and Scalable Multimodal Pathology Retrieval via Attentive Vision-Language Alignment
Hongyi Wang, Zhengjie Zhu, Jiabo Ma, Fang Wang, Yue Shi, Bo Luo, Jili Wang, Qiuyu Cai, Xiuming Zhang, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin, Hao Chen
In this paper, we propose PathSearch, an accurate and scalable multimodal pathology retrieval system that aligns whole slide images and diagnostic reports via attentive vision-language alignment. PathSearch achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple external datasets and demonstrates potential for clinical applications in a multi-cohort reader study.
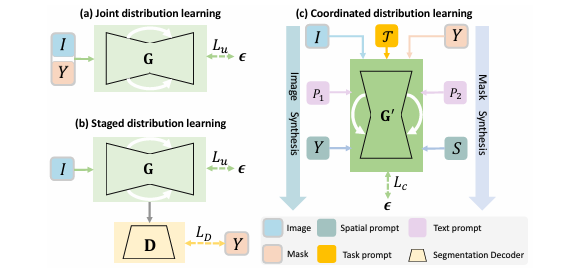
Triple-Prompt Controllable Diffusion for Universal Data Augmentation in Medical Image Segmentation (ECAI 2025)
Shiao Xie, Ke Meng, Hongyi Wang, Liangjun Zhang, Ziwei Niu, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin, Hao Chen
In this paper, we propose TPCDM, a method which can jointly generate paired medical images and masks via a triple-prompt diffusion model, achieving superior synthesis and segmentation.
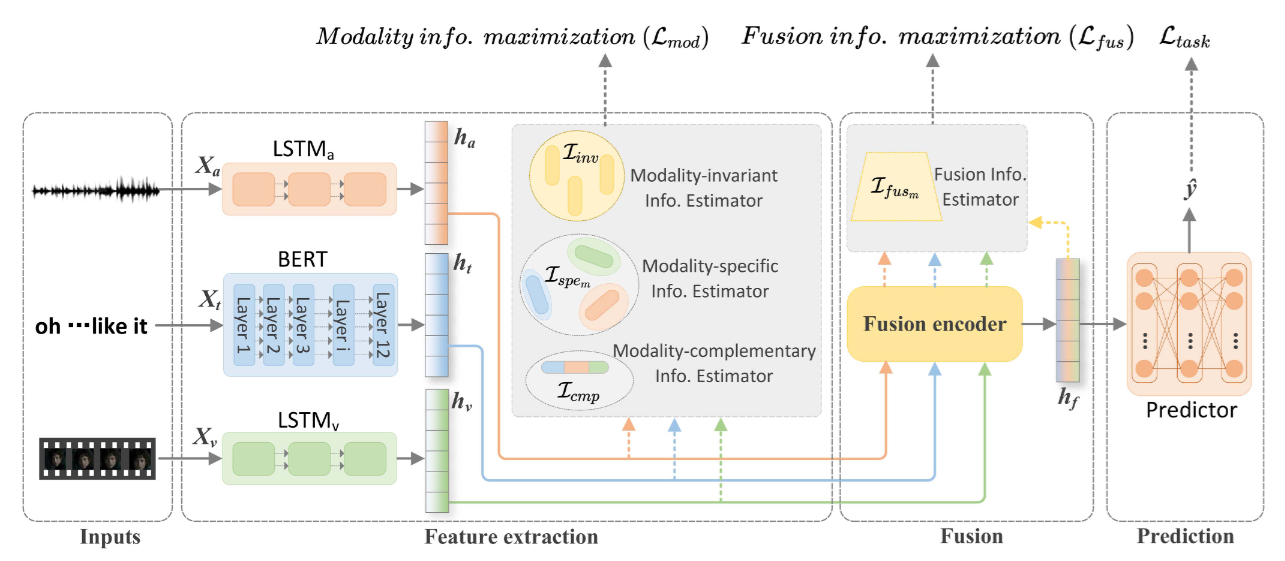
Multimodal sentiment analysis with mutual information-based disentangled representation learning (IEEE TAC 2025)
Hao Sun, Ziwei Niu, Hongyi Wang, Xinyao Yu, Jiaqing Liu, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this paper, we propose a mutual information-based disentangled framework that balances invariant, specific, and complementary features for superior multimodal sentiment analysis.
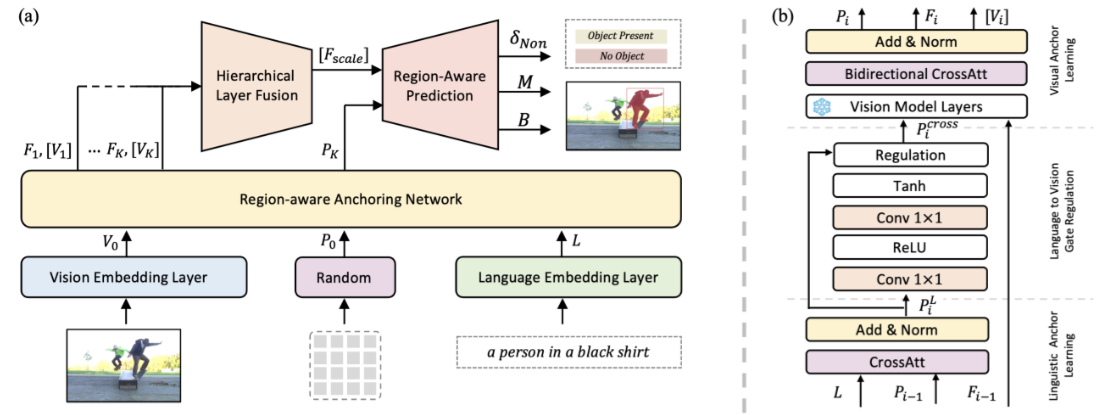
Region-aware Anchoring Mechanism for Efficient Referring Visual Grounding (ICCV 2025)
Shuyi Ouyang, Ziwei Niu, Hongyi Wang, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this paper, we propose RaAM, a region-aware anchoring mechanism for referring visual grounding that enhances multi-target localization, reduces noise, and lowers computation cost.
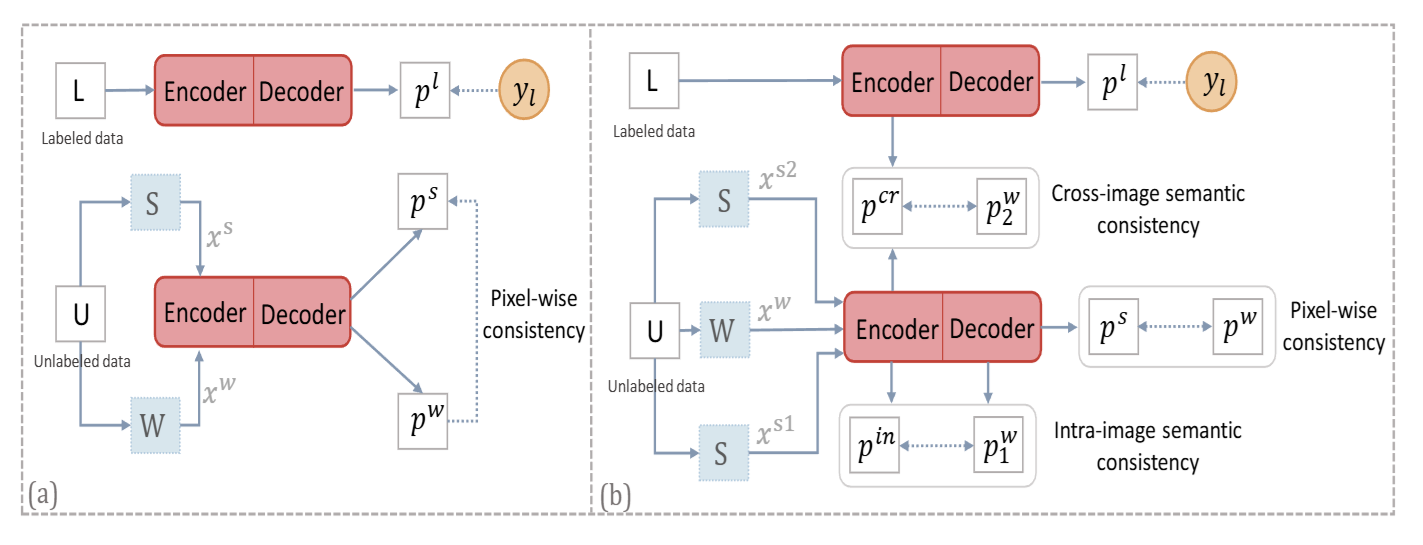
S2Match: Revisiting Weak-to-Strong Consistency from a Semantic Similarity Perspective for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation (JBHI Under Review)
Shiao Xie, Hongyi Wang, Ziwei Niu, Hao Sun, Shuyi Ouyang, Yen-Wei Chen, Lanfen Lin
In this paper, we propose a mutual information-based disentangled framework that balances invariant, specific, and complementary features for superior multimodal sentiment analysis. This work has been formerly released as *SemSim, Revisiting Weak-to-Strong Consistency from a Semantic Similarity Perspective for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation*.
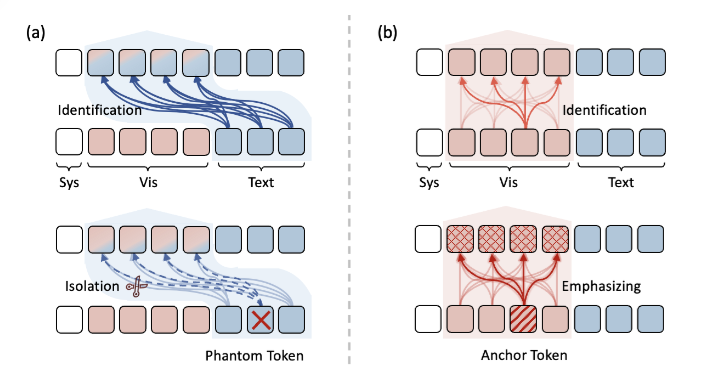
Taming the Phantom: Token-Asymmetric Filtering for Hallucination Mitigation in Large Vision-Language Models (AAAI 2026)
Shuyi Ouyang, Hongyi Wang, Gongfan Fang, Xinyin Ma, Lanfen Lin, Xinchao Wang
In this paper, we analyzed the hallucination issue in large vision-language models and proposed TAF, a token-asymmetric filtering mechanism to mitigate such issue by filtering out potentially problematic image tokens during cross-modal attention. The code will be released upon publication.










